TL;DR:
- AI-CMMI Integration: Framework for developing AI systems using CMMI DEV maturity levels
- Process Adaptation: Mapping AI development lifecycle to CMMI process areas
- Ethical AI Development: Integrating ethics, bias mitigation, and transparency requirements
- Risk Management: Identifying and managing AI-specific risks throughout development
- Quality Assurance: Establishing metrics and validation for AI system reliability
- Security Framework: Implementing comprehensive security measures for AI systems
- Implementation Challenges: Addressing data dependency, computational intensity, and regulatory compliance
Developing AI Systems Using CMMI DEV Strategy
1. Introduction: AI Development in the CMMI DEV Framework
The development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems presents unique challenges that traditional software development frameworks must adapt to accommodate. The Capability Maturity Model Integration for Development (CMMI DEV) provides a structured approach to managing these challenges while ensuring quality, reliability, and ethical considerations.
This comprehensive guide explores how to develop AI systems using the CMMI DEV maturity framework, adapting traditional process areas to accommodate AI-specific requirements such as data management, model validation, ethical considerations, and continuous learning capabilities.
2. Understanding AI Development Characteristics
2.1 Unique Challenges in AI Projects
AI development differs significantly from traditional software development due to several key characteristics:
- Data Dependency: AI models require extensive, high-quality training data that must be collected, labeled, and maintained throughout the model’s lifecycle
- Experimental Nature: AI development involves significant trial and error, with iterative model training and validation cycles
- Ethical Considerations: AI systems must address bias detection, fairness, transparency, and accountability requirements
- Computational Intensity: Resource-intensive training and inference processes requiring specialized hardware and infrastructure
- Continuous Learning: Models may require ongoing updates and retraining to maintain performance as data distributions change
2.2 AI Development Lifecycle
The AI development lifecycle typically includes:
- Problem Definition: Define the AI problem, objectives, and success criteria
- Data Acquisition: Collect, clean, and prepare training data
- Model Development: Design, train, and validate AI models
- Testing and Validation: Comprehensive testing for performance, bias, and safety
- Deployment and Monitoring: Deploy models with continuous monitoring and maintenance
- Feedback and Iteration: Collect feedback and iterate on model improvements
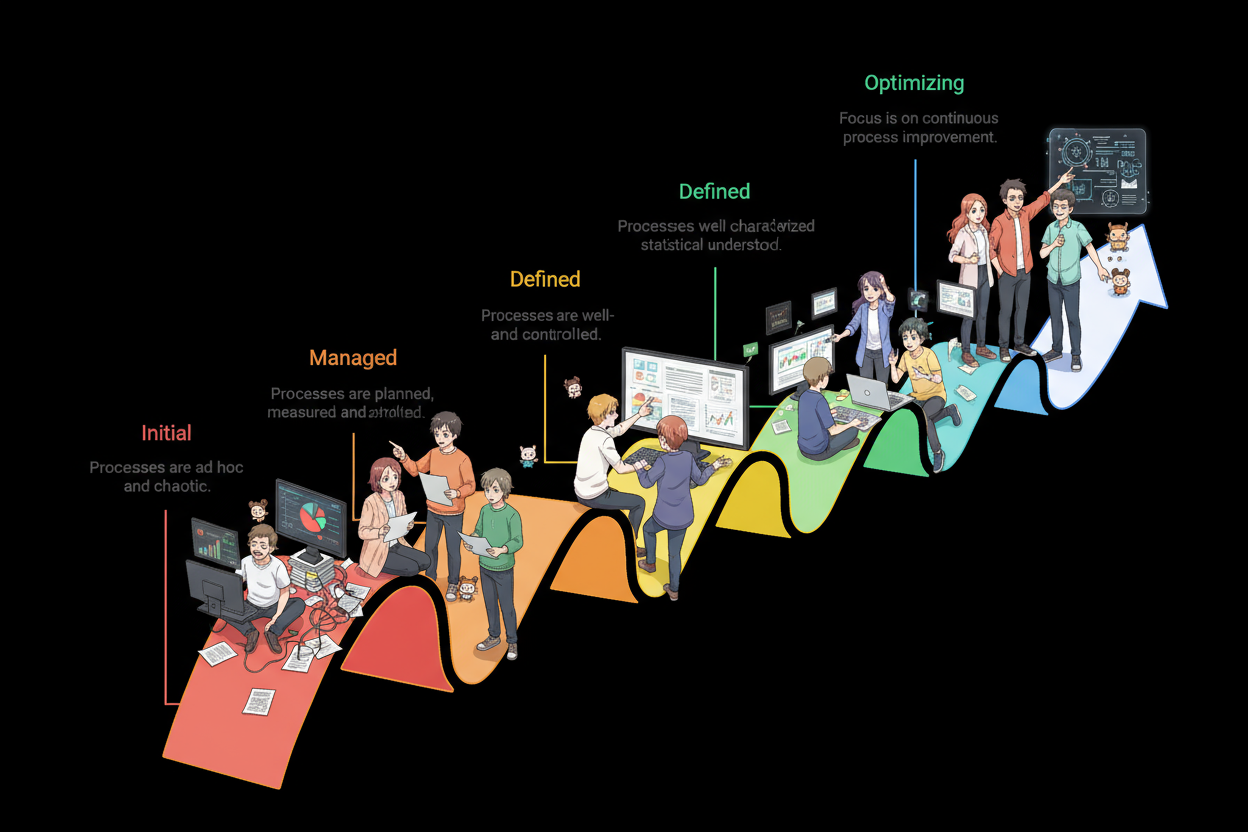
3. Mapping AI Development to CMMI DEV Maturity Levels
3.1 Level 1: Initial (AI Context)
Characteristics in AI Development:
- Ad hoc AI experimentation without structured processes
- Success depends on individual data scientist expertise
- Limited documentation of data sources and model decisions
- High risk of model bias and ethical issues
AI-Specific Goals:
- Recognize the need for structured AI development processes
- Begin documenting data sources and preprocessing steps
- Establish basic version control for models and datasets
3.2 Level 2: Managed (AI Foundation)
Process Areas Adaptation:
| CMMI Process Area | AI-Specific Implementation | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Requirements Management (REQM) | Define AI system requirements, data needs, performance metrics | Include ethical requirements, bias mitigation, explainability |
| Project Planning (PP) | Plan data acquisition, model training schedules, computational resources | Account for experimental phases and iterative model development |
| Project Monitoring and Control (PMC) | Track model training progress, performance metrics, and resource utilization | Monitor for training convergence and computational efficiency |
| Supplier Agreement Management (SAM) | Manage data vendors, cloud computing providers, and AI tool suppliers | Ensure data quality and compliance with licensing agreements |
| Measurement and Analysis (MA) | Establish AI performance metrics, model validation criteria | Include fairness metrics, robustness testing, drift detection |
| Process and Product Quality Assurance (PPQA) | Review AI development processes and model artifacts | Ensure ethical guidelines and bias mitigation practices |
| Configuration Management (CM) | Manage datasets, model versions, training environments | Track data lineage, model artifacts, and deployment configurations |
AI-Specific Goals:
- Establish controlled data collection and preprocessing pipelines
- Implement version control for models, datasets, and training code
- Create standardized metrics for model performance evaluation
- Develop basic documentation for data sources and model decisions
3.3 Level 3: Defined (AI Standardization)
Enhanced Process Areas:
| Additional Process Areas | AI-Specific Implementation | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Requirements Development (RD) | Elicit, analyze, and establish AI system requirements including data, performance, and ethical criteria | Define model interpretability and fairness requirements |
| Technical Solution (TS) | Design AI architecture, select algorithms, and implement model training pipelines | Consider scalability, computational efficiency, and deployment requirements |
| Product Integration (PI) | Integrate AI models with existing systems and ensure proper data flow | Manage API integrations and real-time inference capabilities |
| Verification (VER) | Verify AI model performance against specified requirements | Include unit testing for model components and integration testing |
| Validation (VAL) | Validate AI system performance in operational environments | Conduct user acceptance testing and ethical validation |
| Organizational Process Focus (OPF) | Establish AI development standards and best practices | Create organizational guidelines for AI ethics and responsible development |
| Organizational Process Definition (OPD) | Define standard AI development processes and templates | Develop reusable AI development patterns and checklists |
| Organizational Training (OT) | Provide training in AI development, ethics, and compliance | Ensure team competency in machine learning and data science |
| Integrated Project Management (IPM) | Coordinate AI projects using defined organizational processes | Manage cross-functional teams including data scientists, engineers, and domain experts |
| Risk Management (RSKM) | Identify and manage AI-specific risks including data quality, model bias, and regulatory compliance | Monitor for emerging risks like adversarial attacks and model drift |
| Decision Analysis and Resolution (DAR) | Make informed decisions about AI architecture, algorithms, and deployment strategies | Use data-driven approaches for technology selection and trade-off analysis |
AI-Specific Goals:
- Standardize AI development processes across the organization
- Implement comprehensive data governance and quality management
- Establish ethical review processes for AI systems
- Create reusable AI development templates and checklists
3.4 Level 4: Quantitatively Managed (AI Optimization)
Advanced Process Areas:
| Process Areas | AI-Specific Implementation | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Organizational Process Performance (OPP) | Establish quantitative baselines for AI development performance | Define metrics for model accuracy, training efficiency, and deployment success |
| Quantitative Project Management (QPM) | Manage AI projects using statistical process control | Predict project timelines and resource needs based on historical data |
AI-Specific Goals:
- Establish statistical process control for AI model performance
- Implement predictive analytics for project planning and risk assessment
- Create quantitative baselines for AI development efficiency
3.5 Level 5: Optimizing (AI Innovation)
Process Areas:
| Process Areas | AI-Specific Implementation | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Organizational Innovation and Deployment (OID) | Deploy AI innovations and improvements across the organization | Share successful AI practices and technologies |
| Causal Analysis and Resolution (CAR) | Identify root causes of AI model failures and performance issues | Implement preventive actions for common AI development problems |
AI-Specific Goals:
- Continuously improve AI development processes through innovation
- Implement advanced techniques like automated machine learning (AutoML)
- Foster a culture of AI experimentation and learning
4. AI-Specific Risk Management Framework
4.1 AI Risk Categories
Technical Risks:
- Model overfitting or underfitting
- Data quality and representativeness issues
- Computational resource limitations
- Model deployment and scalability challenges
Ethical and Legal Risks:
- Algorithmic bias and discrimination
- Privacy and data protection violations
- Lack of model interpretability and explainability
- Regulatory compliance issues
Operational Risks:
- Model drift and performance degradation
- System integration and compatibility issues
- Security vulnerabilities in AI systems
- Resource and cost management challenges
4.2 Risk Mitigation Strategies
| Risk Category | Mitigation Strategy | CMMI Process Area |
|---|---|---|
| Data Quality | Implement data validation pipelines and quality checks | Verification (VER), Validation (VAL) |
| Model Bias | Conduct regular bias audits and fairness testing | Process and Product Quality Assurance (PPQA) |
| Model Drift | Establish continuous monitoring and retraining processes | Measurement and Analysis (MA) |
| Regulatory Compliance | Implement compliance frameworks and audit trails | Risk Management (RSKM) |
| Security Vulnerabilities | Apply security best practices throughout development | Configuration Management (CM) |
5. Ethical AI Development Framework
5.1 Integrating Ethics into CMMI DEV
Requirements Development (RD):
- Define ethical requirements including fairness, transparency, and accountability
- Establish criteria for bias detection and mitigation
- Specify requirements for model interpretability and explainability
Verification and Validation (VAL):
- Conduct ethical validation testing
- Perform bias and fairness assessments
- Validate compliance with ethical guidelines and regulations
Organizational Process Definition (OPD):
- Develop organizational ethical guidelines for AI development
- Create checklists for ethical considerations
- Establish review processes for ethical compliance
5.2 Ethical AI Metrics
- Fairness Metrics: Demographic parity, equal opportunity, and disparate impact measures
- Transparency Metrics: Model interpretability scores and explanation quality assessments
- Accountability Metrics: Audit trail completeness and decision traceability
- Privacy Metrics: Data protection compliance and anonymization effectiveness
6. Quality Assurance for AI Systems
6.1 AI-Specific Quality Attributes
Functional Quality:
- Model accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score
- Prediction confidence and uncertainty quantification
- Model robustness to input variations
Non-Functional Quality:
- Inference latency and throughput
- Model size and computational efficiency
- Scalability and resource utilization
Ethical Quality:
- Bias and fairness metrics
- Interpretability and explainability
- Privacy and security compliance
6.2 Testing Strategies for AI Systems
| Testing Type | Description | CMMI Process Area |
|---|---|---|
| Unit Testing | Test individual model components and functions | Verification (VER) |
| Integration Testing | Test model integration with other system components | Product Integration (PI) |
| System Testing | Test complete AI system functionality | Validation (VAL) |
| Performance Testing | Test model performance under various conditions | Measurement and Analysis (MA) |
| Ethical Testing | Test for bias, fairness, and ethical compliance | Process and Product Quality Assurance (PPQA) |
| Adversarial Testing | Test model robustness against adversarial inputs | Risk Management (RSKM) |
7. Security Framework for AI Systems
7.1 AI Security Challenges
AI systems face unique security threats that differ from traditional software:
- Adversarial Attacks: Malicious inputs designed to fool AI models (e.g., adversarial examples)
- Data Poisoning: Tampering with training data to compromise model integrity
- Model Inversion: Extracting sensitive information from trained models
- Evasion Attacks: Bypassing detection systems through carefully crafted inputs
- Model Theft: Unauthorized copying or reverse engineering of proprietary models
- Supply Chain Attacks: Compromising third-party AI components or datasets
7.2 Integrating Security into CMMI DEV Process Areas
| CMMI Process Area | Security Implementation | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Requirements Management (REQM) | Define security requirements, threat models, and compliance needs | Include security requirements in AI system specifications |
| Project Planning (PP) | Plan security assessments, penetration testing, and secure development practices | Allocate resources for security throughout the development lifecycle |
| Configuration Management (CM) | Secure version control for models, datasets, and code | Implement access controls and audit trails for AI artifacts |
| Verification (VER) | Security testing and vulnerability assessments | Conduct security reviews and penetration testing |
| Validation (VAL) | Validate security controls in operational environments | Test security effectiveness in production-like settings |
| Risk Management (RSKM) | Identify and manage AI-specific security risks | Monitor emerging threats and implement mitigation strategies |
| Process and Product Quality Assurance (PPQA) | Security audits and compliance reviews | Ensure security best practices are followed |
7.3 Security Best Practices for AI Development
Data Security:
- Implement encryption for data at rest and in transit
- Use secure data pipelines with access controls
- Conduct data provenance tracking and validation
- Apply differential privacy techniques for sensitive data
Model Security:
- Implement model watermarking and fingerprinting
- Use secure multi-party computation for distributed training
- Apply adversarial training techniques
- Implement model hardening against common attacks
Infrastructure Security:
- Secure cloud environments and AI platforms
- Implement network segmentation and access controls
- Use secure APIs for model deployment
- Monitor for anomalous behavior and intrusions
Development Security:
- Follow secure coding practices for AI code
- Implement code reviews with security focus
- Use automated security scanning tools
- Maintain secure development environments
7.4 Security Testing and Validation
| Testing Type | Description | Tools/Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Adversarial Testing | Test model robustness against adversarial inputs | FGSM, PGD attacks |
| Data Poisoning Testing | Validate data integrity and detect tampering | Data validation frameworks |
| Model Inversion Testing | Assess information leakage risks | Membership inference attacks |
| Evasion Testing | Test detection system bypass attempts | Black-box testing techniques |
| Penetration Testing | Comprehensive security assessment | Manual and automated pentesting |
7.5 Security Monitoring and Incident Response
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement real-time security monitoring for AI systems
- Anomaly Detection: Use AI for detecting security anomalies (with human oversight)
- Incident Response Plans: Develop specific plans for AI security incidents
- Forensic Analysis: Maintain audit logs for incident investigation
- Recovery Procedures: Define model retraining and system recovery processes
7.6 Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
- GDPR and Data Privacy: Ensure compliance with data protection regulations
- AI Security Standards: Follow frameworks like NIST AI RMF
- Industry-Specific Regulations: Comply with sector-specific security requirements
- Audit and Reporting: Maintain security audit trails and reporting capabilities
8. Implementation Roadmap
8.1 Phase 1: AI Readiness Assessment (1-2 months)
- Current State Evaluation: Assess existing AI development capabilities and processes
- Gap Analysis: Identify gaps between current practices and CMMI DEV requirements
- Resource Assessment: Evaluate available data, computing resources, and team skills
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks and mitigation strategies
8.2 Phase 2: Process Adaptation (2-4 months)
- Process Tailoring: Adapt CMMI DEV process areas for AI development context
- Tool Selection: Choose appropriate tools for AI development and process management
- Training Programs: Develop training plans for team members
- Pilot Project: Implement adapted processes in a small-scale AI project
8.3 Phase 3: Full Implementation (4-6 months)
- Organization-wide Rollout: Extend adapted processes across the organization
- Continuous Monitoring: Establish metrics and monitoring systems
- Feedback Integration: Collect feedback and make process improvements
- Certification Preparation: Prepare for formal CMMI DEV appraisal if desired
8.4 Phase 4: Continuous Improvement (Ongoing)
- Performance Monitoring: Track AI development performance and quality metrics
- Process Optimization: Continuously improve AI development processes
- Innovation Integration: Incorporate new AI technologies and methodologies
- Knowledge Sharing: Share lessons learned and best practices
9. Tools and Technologies
9.1 AI Development Tools
Machine Learning Frameworks:
- TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-learn for model development
- Keras, Hugging Face Transformers for high-level model building
- AutoML platforms like Google Cloud AutoML and AWS SageMaker
Data Management Tools:
- DVC (Data Version Control) for dataset versioning
- Apache Spark and Dask for large-scale data processing
- Data validation tools like Great Expectations
9.2 Process Management Tools
CMMI DEV Support Tools:
- IBM Rational for process management and compliance
- CA Agile Central for integrated development management
- VersionOne for unified Agile-CMMI support
AI-Specific Tools:
- MLflow for experiment tracking and model management
- Weights & Biases for model monitoring and visualization
- Comet.ml for model performance tracking
9.3 Quality Assurance Tools
Testing Frameworks:
- DeepTest for AI system testing
- Metamorphic Testing for AI validation
- AI Fairness 360 for bias detection
Monitoring Tools:
- Prometheus and Grafana for model performance monitoring
- Evidently AI for model drift detection
- Fiddler for model explainability and debugging
9.4 Security Tools
Adversarial Testing Tools:
- CleverHans and Foolbox for generating adversarial examples
- ART (Adversarial Robustness Toolbox) for testing model vulnerabilities
Security Scanning Tools:
- Snyk and OWASP ZAP for dependency and code vulnerability scanning
- Bandit for Python security linting
Model Security Tools:
- Fawkes for model watermarking and protection
- CrypTen for secure multi-party computation
Monitoring and SIEM:
- Splunk and ELK Stack for security event monitoring
- Darktrace for AI-powered threat detection
10. Case Study: Financial Services AI Implementation
10.1 Context
A major financial institution implemented AI for fraud detection using CMMI DEV Level 3 processes.
10.2 Implementation Approach
- Requirements Management: Defined comprehensive requirements including fraud detection accuracy, false positive rates, and ethical considerations
- Data Management: Established rigorous data governance processes for sensitive financial data
- Model Development: Used iterative development with continuous validation and bias testing
- Risk Management: Identified and managed risks related to model bias, regulatory compliance, and system security
- Quality Assurance: Implemented comprehensive testing including adversarial testing and ethical validation
- Security Implementation: Integrated security controls, threat modeling, and penetration testing
10.3 Results
- Fraud Detection Accuracy: 40% improvement in fraud detection while reducing false positives
- Development Efficiency: 30% reduction in time-to-deployment through process standardization
- Compliance: Maintained regulatory compliance while accelerating AI innovation
- Ethical Performance: Achieved 99.5% model accuracy with comprehensive bias mitigation
- Security Performance: Achieved zero security incidents during initial deployment
10.4 Key Success Factors
- Integrated AI ethics and governance into core development processes
- Established cross-functional teams combining domain expertise with AI skills
- Implemented automated monitoring and alerting systems
- Maintained rigorous testing and validation protocols throughout development
- Integrated security throughout the development lifecycle
11. Challenges and Solutions
11.1 Common Challenges
| Challenge | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Data Quality Management | Ensuring data quality and representativeness for AI training | Implement automated data validation pipelines and quality gates |
| Model Interpretability | Making complex AI models understandable and explainable | Use interpretable AI techniques and documentation standards |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating complex regulatory requirements for AI systems | Develop compliance frameworks integrated with development processes |
| Skill Gap | Lack of AI expertise in development teams | Invest in comprehensive training programs and strategic hiring |
| Computational Resources | Managing high computational requirements for AI development | Optimize resource allocation and use cloud-based solutions |
| Security Vulnerabilities | Protecting AI systems from adversarial attacks and data breaches | Implement comprehensive security testing and monitoring |
11.2 Best Practices
Organizational Level:
- Establish AI governance boards for oversight and ethical guidance
- Develop comprehensive data strategies and governance frameworks
- Invest in AI skills development and certification programs
- Build scalable AI infrastructure and deployment platforms
- Implement organization-wide security policies for AI systems
Project Level:
- Integrate ethical considerations into all process areas
- Implement automated bias detection and mitigation processes
- Ensure model explainability and auditability
- Establish continuous monitoring and improvement processes
- Apply security best practices throughout the AI development lifecycle
Technical Level:
- Implement MLOps practices for automated deployment and monitoring
- Use specialized tools for model and data versioning
- Develop comprehensive testing suites for AI validation
- Apply security best practices throughout the AI lifecycle
12. Measuring Success
12.1 Technical Metrics
- Model accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score
- Training time and computational efficiency
- Model size and inference latency
- Bias and fairness assessment scores
- Security vulnerability assessment scores
- Adversarial robustness metrics
12.2 Process Metrics
- Time-to-deployment for AI models
- Defect rates in AI system development
- Compliance with ethical and regulatory standards
- Team productivity and learning curves
- Security incident rates and response times
12.3 Business Metrics
- Return on investment from AI implementations
- Customer satisfaction with AI-powered features
- Competitive advantage gained through AI capabilities
- Innovation pipeline strength and success rate
13. Future Directions
13.1 Emerging Trends
- AutoML Integration: Incorporating automated machine learning into CMMI DEV processes
- Edge AI Development: Adapting processes for edge computing and IoT applications
- Federated Learning: Managing distributed AI development across multiple organizations
- AI Ethics Automation: Implementing automated ethical assessment and compliance tools
- AI Security Automation: Implementing automated security testing and monitoring for AI systems
13.2 Research Directions
- AI Process Maturity Models: Developing AI-specific maturity frameworks
- Ethical AI Metrics: Establishing standardized metrics for AI ethics and fairness
- Regulatory Frameworks: Adapting CMMI DEV for emerging AI regulations
- Sustainable AI: Integrating environmental impact considerations into AI development processes
- AI Security Frameworks: Developing comprehensive security frameworks for AI systems
14. Conclusion
Developing AI systems using the CMMI DEV strategy provides a structured approach to managing the unique challenges of AI development while ensuring quality, ethics, security, and regulatory compliance. By adapting traditional software development processes to accommodate AI-specific requirements, organizations can achieve higher maturity levels and deliver more reliable, ethical, secure, and effective AI solutions.
The key to success lies in understanding the unique characteristics of AI development and thoughtfully integrating them with proven process improvement frameworks. Organizations that successfully implement this approach will be better positioned to leverage AI’s transformative potential while managing associated risks, ethical considerations, and security threats.
15. References
- CMMI Institute Official Website
- Software Engineering Institute (SEI) CMMI Resources
- “CMMI for Development, Version 1.3” - Chrissis, Konrad, Shrum
- IEEE Standard for Artificial Intelligence (AI) Model Documentation
- NIST AI Risk Management Framework
- European Commission’s AI Ethics Guidelines
- Google’s Responsible AI Practices
- Microsoft’s AI Ethics Principles
- “Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach” - Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig
- AI Fairness 360 Toolkit
- MLflow Documentation
- DVC (Data Version Control) Documentation
- OWASP AI Security
- CISA AI Security Best Practices
- IBM AI Security Guide
This guide is based on CMMI for Development Version 1.3 and current AI development best practices. Organizations should consult the latest versions of both frameworks and relevant regulatory requirements for their specific context.